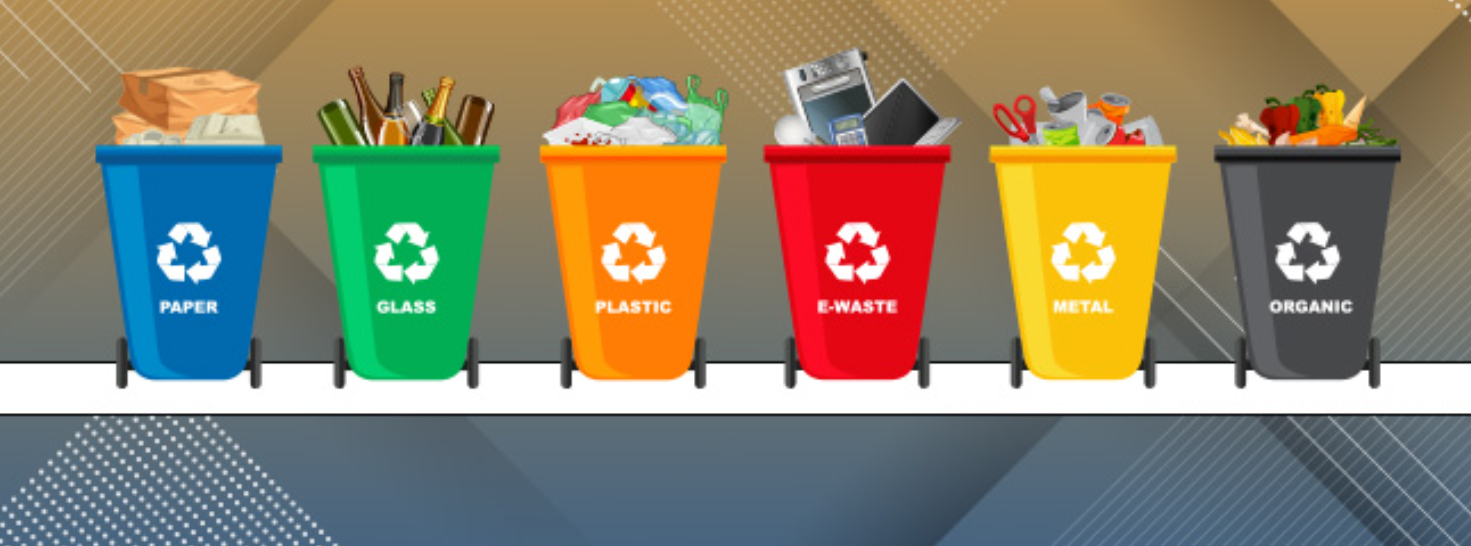
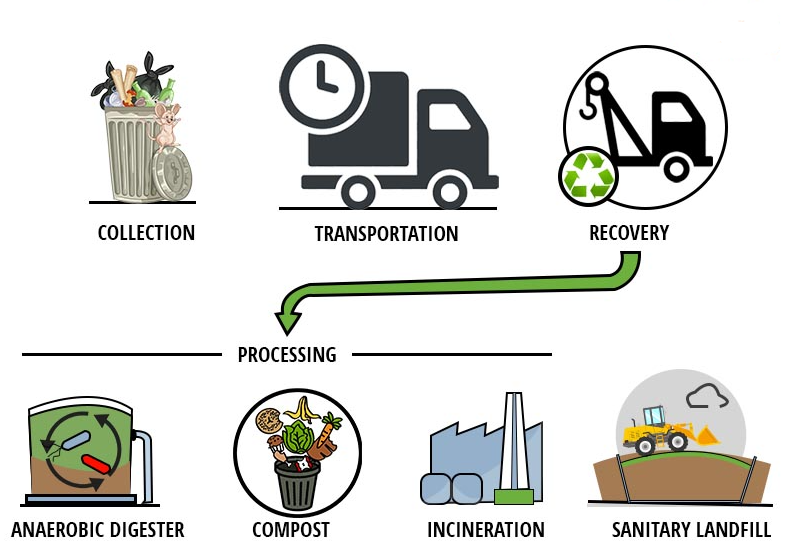
Solid waste management is the process of collecting, treating, disposing of, and recycling solid waste generated by human activities to minimize its environmental impact and promote public health. Solid waste includes a wide range of materials, such as household waste, commercial waste, industrial waste, construction and demolition debris, and agricultural waste. Proper solid waste management is essential to prevent pollution, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, conserve resources, and create a clean and healthy environment. Here are the key components and objectives of solid waste management: Components of Solid Waste Management: Waste Collection: The first step in solid waste management is the collection of waste from various sources, such as households, businesses, and institutions. Waste is collected through curbside collection, drop-off points, or waste bins located in public areas. Waste Segregation: After collection, waste is sorted and segregated into different categories, such as organic waste, recyclables (paper, plastic, glass, metals), and non-recyclable or hazardous waste. Waste Treatment and Recycling: Recyclable materials are sent to recycling facilities to be processed and transformed into new products. Organic waste can be composted to produce nutrient-rich compost for agriculture. Some types of hazardous waste may undergo special treatment or disposal to minimize their environmental impact. Waste Disposal: Non-recyclable and non-compostable waste is disposed of in landfills or waste-to-energy facilities. Landfills are designed to prevent environmental contamination and manage the decomposition of waste. Waste-to-Energy Conversion: In waste-to-energy facilities, non-recyclable waste is incinerated to generate electricity or heat, reducing the volume of waste sent to landfills and harnessing energy from waste. Public Awareness and Education: Public awareness campaigns and educational programs are essential to encourage waste reduction, recycling, and responsible waste disposal practices among the general population. Objectives of Solid Waste Management: Waste Reduction: The primary objective of solid waste management is to reduce the generation of waste and promote waste minimization at the source. Resource Conservation: Recycling and reusing materials from waste help conserve natural resources and reduce the need for raw materials. Environmental Protection: Proper waste management prevents pollution, soil contamination, and water pollution, safeguarding the environment and ecosystems. Public Health Protection: Effective waste management prevents the spread of diseases and pests associated with uncontrolled waste disposal. Greenhouse Gas Emission Reduction: Proper waste management, including waste-to-energy conversion, can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions from decomposing waste in landfills. Circular Economy Promotion: Implementing waste management practices that promote recycling and circular economy principles contribute to a more sustainable and resource-efficient economy. Land Conservation: Proper landfill management ensures the responsible use and conservation of land for waste disposal. Solid waste management is a complex and ever-evolving process that requires a combination of technological solutions, policy frameworks, public participation, and continuous innovation to address the challenges of growing waste generation and environmental sustainability. Integrated waste management systems that prioritize waste reduction, recycling, and resource recovery are vital for a sustainable and greener future.