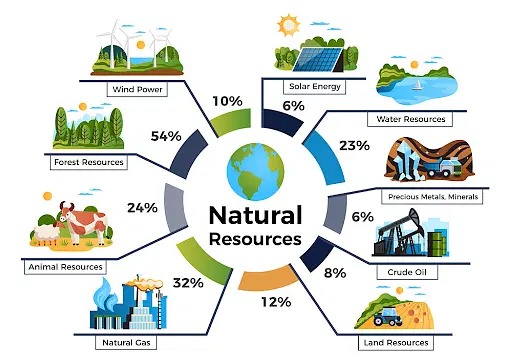
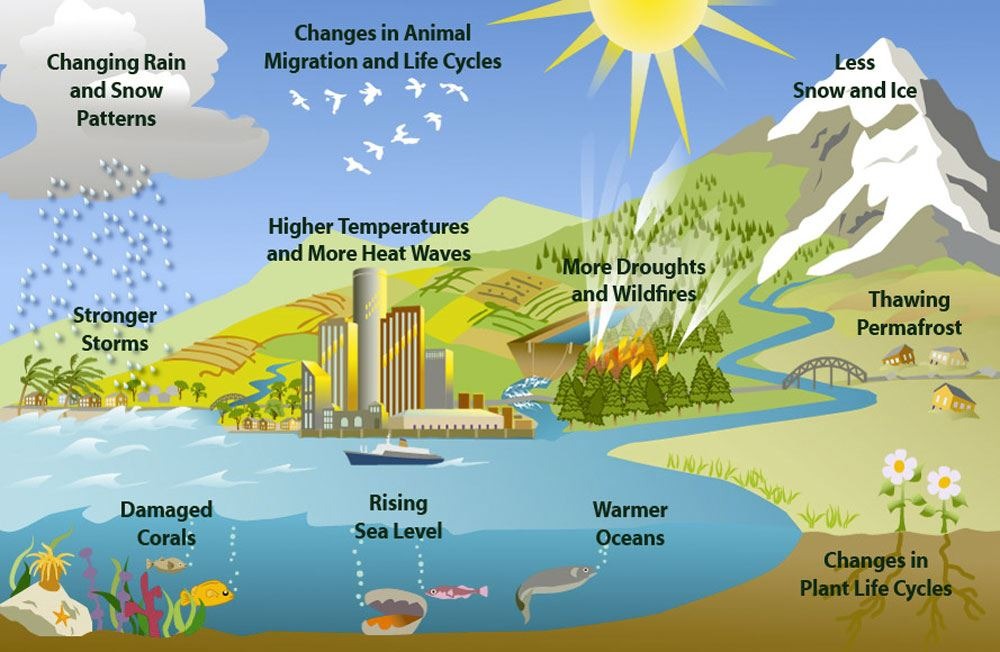
Natural Resource Management (NRM) refers to the sustainable utilization of major natural resources, such as land, water, air, minerals, forests, fisheries, and wild flora and fauna. Together, these resources provide the ecosystem services that provide better quality to human life.Natural Resource Management (NRM) refers to the sustainable utilization of major natural resources, such as land, water, air, minerals, forests, fisheries, and wild flora and fauna. Together, these resources provide the ecosystem services that provide better quality to human life.
Natural resource management (NRM) refers to the sustainable and responsible management of natural resources, including land, water, forests, minerals, and biodiversity. It involves the planning, conservation, utilization, and equitable distribution of natural resources to meet present and future needs while maintaining ecological integrity. Here are some key aspects of natural resource management:
Resource assessment and monitoring: Understanding the status and trends of natural resources is crucial for effective management. Resource assessments and monitoring programs help evaluate the availability, quality, and sustainability of resources. This information guides decision-making and enables the identification of potential threats and opportunities.
Sustainable land management: Land is a valuable natural resource that needs to be managed sustainably. This includes implementing practices such as soil conservation, reforestation, agroforestry, terracing, and sustainable agriculture to prevent soil erosion, land degradation, and loss of biodiversity. Land-use planning and zoning can help balance competing demands and ensure responsible land management.
Water resource management: Water is a vital resource that requires careful management. This involves ensuring equitable access to water, protecting water sources, promoting water conservation, and implementing sustainable water use practices. Integrated water resource management considers the interconnections between water availability, quality, and ecosystem health.
Forest management: Forests provide numerous ecosystem services and are essential for biodiversity conservation, climate regulation, and livelihoods. Sustainable forest management involves practices like selective logging, reforestation, protected area management, and community-based forest management. It aims to balance economic, social, and environmental benefits while preserving forest ecosystems.
Biodiversity conservation: Biodiversity is crucial for ecosystem resilience and provides important ecological, economic, and cultural values. Conservation measures include the establishment and management of protected areas, habitat restoration, species monitoring, and the promotion of sustainable use practices. Biodiversity conservation also involves addressing the drivers of biodiversity loss, such as habitat destruction and invasive species.
Energy and mineral resource management: The extraction and utilization of energy and mineral resources have significant environmental and social impacts. Responsible management includes measures to minimize environmental damage, promote energy efficiency and renewable energy, ensure worker safety, and support local communities affected by resource extraction.
Stakeholder engagement and participation: Effective natural resource management requires the involvement of diverse stakeholders, including local communities, indigenous peoples, governments, NGOs, and the private sector. Stakeholder engagement processes promote inclusive decision-making, enhance local knowledge and perspectives, and foster ownership and cooperation.
Policy and regulatory frameworks: Sound policies and regulations provide the foundation for sustainable natural resource management. This includes developing legal frameworks, guidelines, and incentives that promote sustainable practices, enforce environmental standards, and ensure equitable resource distribution. Adequate governance structures and enforcement mechanisms are essential for effective implementation.
Integrated and adaptive management approaches: Natural resource management should take an integrated and adaptive approach that considers the interconnectedness of different resources and sectors. Adaptive management involves continuously learning and adjusting strategies based on monitoring results and changing conditions. It embraces the principles of resilience, flexibility, and learning-by-doing.
Effective natural resource management is crucial for maintaining the health and well-being of both ecosystems and human societies. By employing sustainable practices and considering long-term ecological and social factors, NRM seeks to ensure the wise use and conservation of natural resources for present and future generations.